Excel in GCE O-Level Mathematics
Unpack the 3 big content areas you’ll want to master for your O-Level Maths success.
Hello Sec 4 students! The GCE O-Level Mathematics exam is looming ahead, and we know it can feel daunting. But here’s the good news: with the right preparation, you can tackle it with confidence.
In our recent O-Level Prep & Exam Strategies Webinar Series, we went through the O-Level Maths exam and syllabus requirements, common challenges, and tips to prepare for and do well in the exams. We’ll be recapping it all in this article!
Latest Changes to the O-Level Mathematics Syllabus
In 2023, the Ministry of Education introduced a new scheme of assessment for the GCE O-Level Mathematics (Syllabus 4052). Understanding the structure of the paper, the types of questions asked, and the weightage of different topics will allow students to refine their revision strategies and approach the examination with confidence.
Under Syllabus 4052, both Papers 1 and 2 now have the same duration and mark allocation. It is no longer the case that Paper 1 focuses more on fundamentals, and Paper 2 more on higher order thinking skills. Both papers can now test on higher order thinking skills.
The subject syllabus is grouped into three broad content strands as follows:
Numbers and Algebra
Geometry and Measurement
Statistics and Probability
The topics under each content strand is outlined as follows:
To provide students with a clearer understanding of the weightage for each content strand in the O-Level Mathematics exam, we have outlined the percentage distribution as follows:
The Numbers and Algebra strand carries the highest weightage, while the Probability and Statistics strand has the lowest.
A Closer Look at the Three Essential Strands in GCE O-Level Mathematics
In the GCE O-Level Mathematics exam, questions are based on three main content strands: Numbers and Algebra, Geometry and Measurement, and Statistics and Probability. Each strand presents unique concepts and challenges that require students to master and tackle.
Strand I - Numbers and Algebra
Questions from this category carry the highest weightage in the exam. Students are strongly advised to reinforce their understanding of the topics in this category. Given its significance, proficiency in this area also positively impacts other topics. Students who may not be confident in algebra should dedicate time to revising and practicing algebra, as it will greatly benefit their performance in both Paper 1 and Paper 2.
As you practise on algebra-related drills, you should be comfortable with handling a variety of algebraic expressions/equations/inequalities, including algebraic fractions. Master the related techniques including quadratic formula, completing the square and changing the subject of a formulae.
Besides algebra, there are also other topics, including on prime factorisation/ highest common factor/lowest common multiple, and direct and inverse variation, which you should refresh, since these were done at the lower secondary levels, but often do get featured in the O level examinations.
Last, but not least, graph drawing is an integral skill to perfect through practice, as the questions associated with this topic will typically be quite standard, including drawing of curve, drawing tangent and finding gradient, and drawing an additional line through manipulation of the equation of the curve.
Strand II – Geometry and Measurement
Students must pay close attention to the diagrams provided in Geometry and Measurement questions and identify key information that will aid in solving the problem. Take note of the following:
Revise polygons and make sure you remember the formula for calculating the sum of interior angles, and sum of exterior angles. Many students tend to become “rusty” in this topic, as it was done in lower secondary, so a refresher is definitely a must!
Properties of circles may appear overwhelming to some, but the best way to tackle this topic is to make sure that all the symmetrical properties and angle properties of circles are at your fingertips. Look carefully at the diagram to get a sense/hint of the properties that are being tested – for e.g., a diameter points to “angles in a semicircle”, while a tangent suggests that we should be looking out for a right angle between the tangent and the radius.
Congruence and similarity is a core topic that is often interlinked with other topics including Vectors, and Trigonometry, so make sure you build a strong foundation in this topic. Be familiar with all the tests for congruency and similarity, and do not mix them up. Understand how to apply these concepts in problem-solving – calculating the area and volume of similar figures is a particularly common question type.
Strand III – Statistics and Probability
In the final category, students are assessed on their ability to interpret data presented in various forms of statistical diagrams. Make sure you can do the following:
Identify misleading features in a diagram and explain why they lead to misinterpretation of data (for e.g., vertical axis does not start from zero, thereby exaggerating differences in the diagram);
Comparison of data across different diagrams – this typically involves two comparisons, either mean/standard deviation or median/inter-quartile range. Do not simply describe the data, but also interpret what they mean – for e.g., a higher standard deviation indicates the data has a wider spread.
Familiarise yourself with commonly featured diagrams such as the cumulative frequency diagrams and box-and-whisker plots, and how to draw relevant information from them. These include median, upper and lower quartile, and inter-quartile range (commonly asked in exams).
Tackling Problems in Real-World Contexts (PRWC)
In addition to topic-based problems, Problems in Real-World Contexts (PRWC) are also tested in both Papers 1 and 2 of the GCE O-Level Mathematics exam. The last question in Paper 2 is a high-mark weightage, extended PRWC question, which requires a decision to be made.
PRWC questions typically present problems based on real-life situations, requiring students to analyse data from tables, graphs, and other forms of representation. These include scenarios such as transport schedules, travel/excursion plans, and taxation.
To do well for these questions, you should:
1. Analyse the Scenario
Read the question carefully, highlight key data, and identify what you need to find. This avoids misreading and ensuring context understanding. For example, in a finance question, highlighting the principal amount and interest rate ensures you don’t miss critical details, reducing errors. PRWC questions also tend to include distractor information that is not needed in the solution – it is important for you to differentiate between what is needed and what is not.
2. Plan and Solve
Choose the right mathematical approach, based on the concept tested in the problem (e.g., use the compound interest formula where it concerns calculation of compound interest on bank deposits), figure out any assumptions that have to be made and show all steps clearly. Remember that method marks are still awarded for correct methods even if the final decision is incorrect.
The question is also based in a few parts, where the first few parts are easier to score in. Read the context clearly and get these low hanging fruits right, as this will also build momentum towards the last question on decision making.
3. Verify and Interpret
Check your calculations for errors, then ensure your answer fits the context by asking, “Does this make sense?” For example, if a travel time calculation results in a negative value, re-evaluate your steps. This reduces careless mistakes, ensures practicality, and aligns with the need to interpret results in context.
Overcoming Common Challenges in the O-Level Mathematics Exam
Many students face a range of challenges during the GCE O-Level Mathematics exam, which can impact their ability to perform well. In this section, we will delve into some of the most common obstacles students encounter, offering insight into how these challenges can be addressed effectively.
Poor Foundation in Lower Secondary
A weak grasp of lower secondary math, especially algebra, can confuse students in upper secondary, making advanced topics harder. Revisiting and strengthening foundational topics helps build confidence for the exam.Mental Blocks and Difficulty Remembering Formulas
Forgetting formulas under exam pressure is common, often due to insufficient practice under timed conditions. Regularly reviewing formulas and simulating exam scenarios can help students stay sharp and reduce anxiety.Ineffective Time Management
Spending too much time on difficult questions, like 10-mark problems, can leave easier ones unfinished. Students should allocate no more than 15 minutes for such questions and practice with timed past papers to improve pacing and ensure better coverage.Careless Mistakes and Errors in Presentation
Rushing can lead to calculation errors, wrong units, or missing workings, all of which cost marks. Double-checking answers and presenting work clearly, with all steps shown, ensures accuracy and maximises scores. Paying attention to accuracy, units and proper presentation is necessary to avoid loss of marks.
Preparing for the Exam
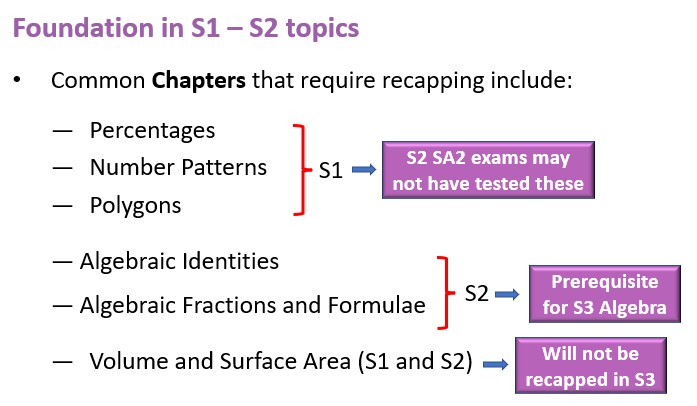
As the O-Level Mathematics exam approaches, it’s important to revisit the foundational topics that are most commonly tested. Here, we outline key topics that students should revisit en route to the GCE O-Level exam, from lower secondary.
By focusing on these topics, students can solidify their understanding, and identify any gaps in knowledge.
Practice is key to mastering O-Level Mathematics. We encourage students to work through the topical Ten-Year-Series (TYS) to refine their skills and build confidence in tackling exam questions. This not only helps familiarise them with common question trends but also improves their ability to apply concepts effectively.
For additional practice, students who have completed the TYS can attempt questions from school Prelim papers. The more exposure they have to different question types, the better prepared they will be for the exam.
As you sit for the exam, here are some key tips to ensure you maximise your marks:
Show Your Workings for Multi-Mark Questions
For questions worth more than one (1) mark, always support your final answer with clear workings. This is crucial as marks are awarded not just for the correct final answer but also the logical steps to get there.Familiarise Yourself with the Formulas
Even though the formula sheet is provided during the exam, it is still essential for students to familiarise themselves with the key mathematical formulas beforehand, so that you know what formula to use for different question types. It is also important to know what formula is in or out of the formula list.Bring Your Geometrical Set
Always remember to bring your curve ruler/construction set for the exams, as it is necessary for questions such as graph drawing.Provide Final Answers to the Correct Precision
When providing your final answers, always ensure they are expressed to 3 significant figures, or 1 decimal place for angles, if the answer is not an exact value, and when the degree of accuracy is not prescribed in the question.
Smart Calculator Use for Exam Success
The use of calculators in the GCE O-Level Mathematics exam is a valuable advantage that students should fully utilise to enhance their accuracy and efficiency. A well-handled calculator can save time, minimise computation errors, and help verify answers.
In this section, we share essential tips on how to make the most of your calculator, from mastering its key functions to ensuring proper usage during the exam.
Know useful calculator functions to check answers, specifically for i) solutions of quadratic equations, ii) solutions of simultaneous equations, and iii) mean and standard deviation for grouped and ungrouped data. That said, even as you use the calculator, ensure that the full workings for these problems are written out clearly, so that you can get the full working marks.
Ensure the correct mode (DEG or RAD) is set when tackling trigonometry questions. This is critical, as some students are known to have lost many marks due to an erroneous setting on their calculator
By familiarising yourself with the updated exam format, key assessment objectives, and common pitfalls, you can navigate the changes effectively. Stay proactive, practice consistently, and achieving success in your O-Level Mathematics is well within your reach!